According to some experts, the achievement of the objectives set in the energy transition for a reduction in greenhouse gases from the sector automotive cannot be achieved solely through theelectrification of cars due to the obvious structural, economic and logistical problems that this would entail, of which we are already partly experiencing the first effects.
It is therefore necessary to develop alternative energy solutions to support to the electricity needed to power electric cars, BEVs (Battery Electric Vehicles). How? Through fuels “decarbonized” – also called e-fuel – the combustion of which does not lead to an increase in CO2 in the atmosphere.
Synthetic fuels e-fuel who produces them
It is therefore the companies themselves that are committed to the research and production of alternative fuelswith the awareness that the full switch to electric could lead to serious problems for the manufacturers themselves, such as a sharp drop in employment and potentially even the survival of some brands.
Already in 2014 Audi had begun to experiment with this new type of fuel. At the time it was obtained thanks to the interactions of genetically modified microbes in South America, precisely in Mexico, where the laboratory tests were carried out.
Toyota for example, research has been ongoing for years onhydrogenWhile Porsche (hence the VW group), through theAD Oliver Blumehad put the spotlight on the need for the development of e-fuels. In particular, the manager of the prestigious German company underlined the importance of alternative fuels for achieving the environmental objectives set by Porsche. Also Mazda promotes e-Fuels to reduce CO emissions2through an approach multi-solution.
Much is being counted on the traction of the‘aeronautical industryfor which the use of e-fuel will be essential. It is estimated that the price per liter could drop from the current 10 dollars to 2 dollarsmaking it affordable for motorists too.
e-Fuel? What are synthetic fuels
The e-fuelalso called electrofuel powerfuel Power-to-X (PtX)can give a new chance for thermal engines in the energy transition. These types of fuels are combustibles liquid or gaseousof synthetic origin, produced through energy-intensive processes powered by renewable electrical energy.

E-fuels are the end result of the process of transforming renewable electrical energy into chemistry in the form of fuels that can be used as energy vectors.
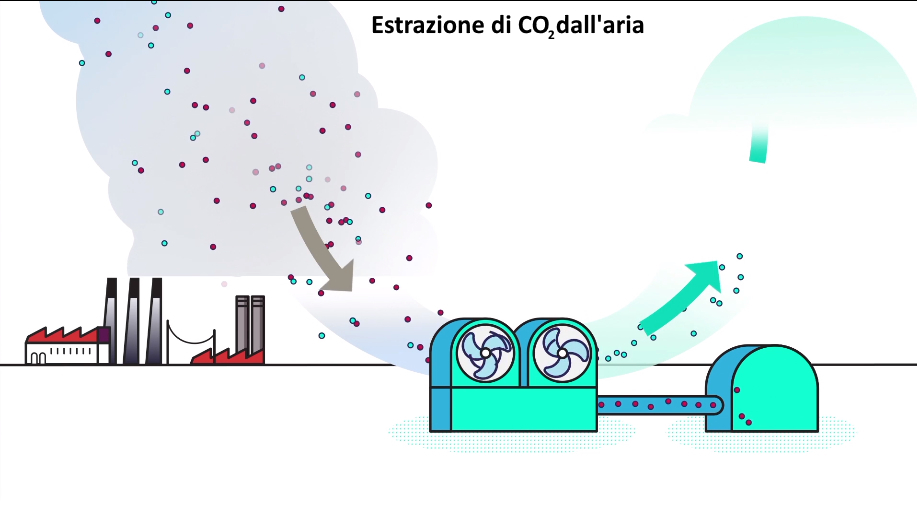
Air to fuel fuel, how e-petrol is produced
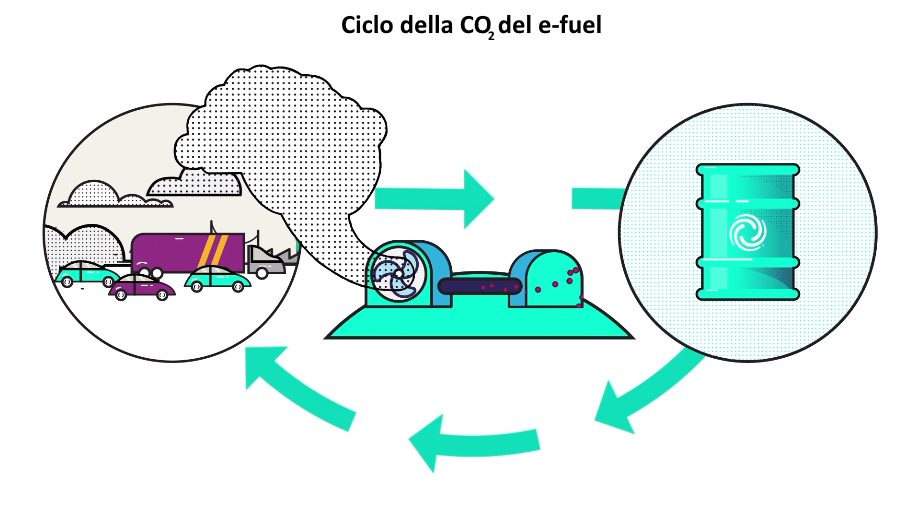
The carbon dioxide (CO2) is combined with thehydrogen to produce zero-impact fuel, as the hydrogen is extracted through electrolysis powered by renewable energy. This process, also known as air to fuelas already mentioned, involves a closed circle for CO2.
The reaction produces methanol (CH3OH)or rather “e-methanol” because it is produced without greenhouse gas emissions. With a further process we arrive at the e-petrolwhose combustion in internal combustion engines does not produce sulfur oxide or other substances harmful to health produced by fossil fuels.
Practically the‘carbon dioxidereleased into the atmosphere following the combustion of traditional fossil fuels, is extracted from the air and transformed into “renewable” fuel which can be used in maritime, air and road transport, without requiring modifications to the vehicle fuel system.
It is also possible to mix this new fuel with petroleum-derived fuels, as is currently the case with biodiesel.
E-fuels pros and cons
The biggest pros of synthetic fuels e-fuel is represented by the fact that they can make any thermal vehicle clean and environmentally friendly, without any mechanical modification. Furthermore, they can be distributed in existing filling stations. But before we get to this scenario there are many critical issues to overcomestarting from the skepticism of many car manufacturers focused exclusively on electric.
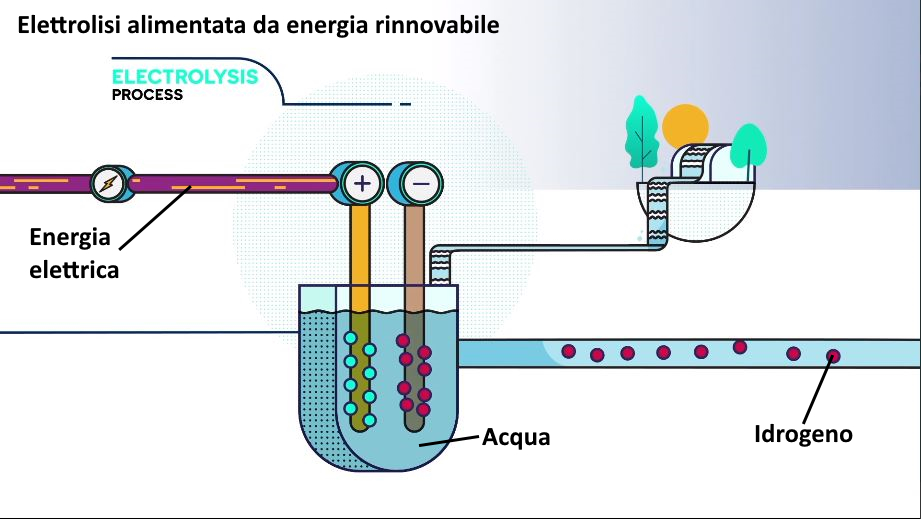
Then there are some against who reside in the electrolysis technology and in the extraction of carbon dioxide from the air which are energy-intensive processes. So to produce a truly high-performance fuel zero impact it is necessary to power the production plants with renewable energyproduced from wind, solar photovoltaic or hydroelectric sources.
It is estimated that an e-fuel production plant could extract up to a million tons of carbon dioxide per yearso to have a significant impact on the percentage of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere many thousands of production sites of this type would be necessary.

Mixing hydrogen with the CO2 you will get synthetic fuelwhich will therefore have a closed cycle with regard to carbon dioxide (carbon neutral fuel), meaning that once burned it will not release new CO2 into the atmosphere, as happens when we burn fossil fuels.
High Innovative Fuels Consortium
Porsche, in collaboration with Enel, Siemens and some oil companies, founded the consortium High Innovative Fuelsand is building an industrial site in Chile dedicated to the production of hydrogen and e-fuels, powered by renewable energy. Among the international partners there is also a piece of Italy with Enelas well as Siemens Energy, Porsche and HIF, ExxonMobil, Gasco and ENAP.
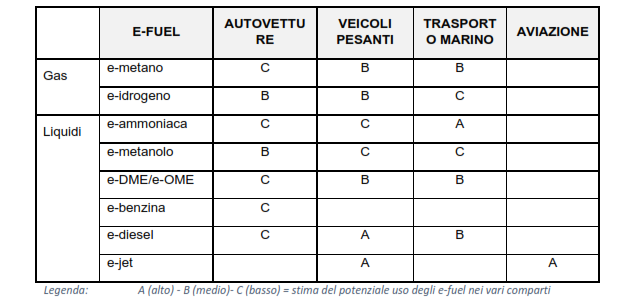
Possible use of e-fuel in the transportation sector segments
Read also:
→ E-fuel synthetic gasoline in Formula 1
→ Stop 2035 sale of thermal cars
→ Energy transition: where are we at?
→ How to reduce CO2 emissions according to Mazda
→ EV Driving all about sustainable mobility
→ What do you think? Take a look at the discussions on the FORUM!
#Efuel #synthetic #fuels #egasoline