Cybersecurity researchers have made light on a new version of a ransomware strain called HardBit, which is distributed with new obfuscation techniques to discourage analysis efforts.
HardBit: How does version 4.0 differ from previous versions?
“Unlike previous versions, HardBit Ransomware group has enhanced version 4.0 with passphrase protection“, they have said cybersecurity researchers Kotaro Ogino and Koshi Oyama in an analysis. “The passphrase must be provided during runtime for the ransomware to execute successfully. Further obfuscation hinders security researchers in analyzing the malware.”
HardBit, emerged for the first time in October 2022, it was created by people who are financially motivated so much so that, HardBit, similarly to other ransomware groups, operates with the aim of generating illicit revenue through double extortion tactics.
What sets this group of cybercriminals apart is that they do not operate a data leak site, but instead pressure victims to pay up by threatening to conduct further attacks in the future; Its primary means of communication is through the instant messaging service Tox.
What is the infection vector of HardBit?
The exact initial access vector used to breach the environments it targets is currently unclear, although it is suspected to involve brute-forcing of RDP and SMB services.
Next steps include credential theft using tools like Mimikatz and NLBrute, and network discovery using utilities like Advanced Port Scanner, allowing attackers to move laterally across the network via RDP.
“After compromising a victim host, the HardBit ransomware payload is executed and goes through a series of steps that reduce the host’s security capabilities before encrypting the victim’s data.“, has said Varonis in his technical report on HardBit 2.0 last year.
Encryption of victim hosts is performed by distributing HardBit, which is delivered using a virus known as Neshta; it is important to note that Neshta has been used in the past by cyber criminals also for distribute Big Head ransomware.
Disabling Microsoft Windows Defender on Microsoft Windows Operating Systems
HardBit is also designed to disable Microsoft Defender Antivirus and terminate processes and services to evade potential detection of its activities and inhibit system recovery; it then encrypts files of interest, updates their icons, changes the desktop background, and modifies the system volume label with the string “Locked by HardBit.”
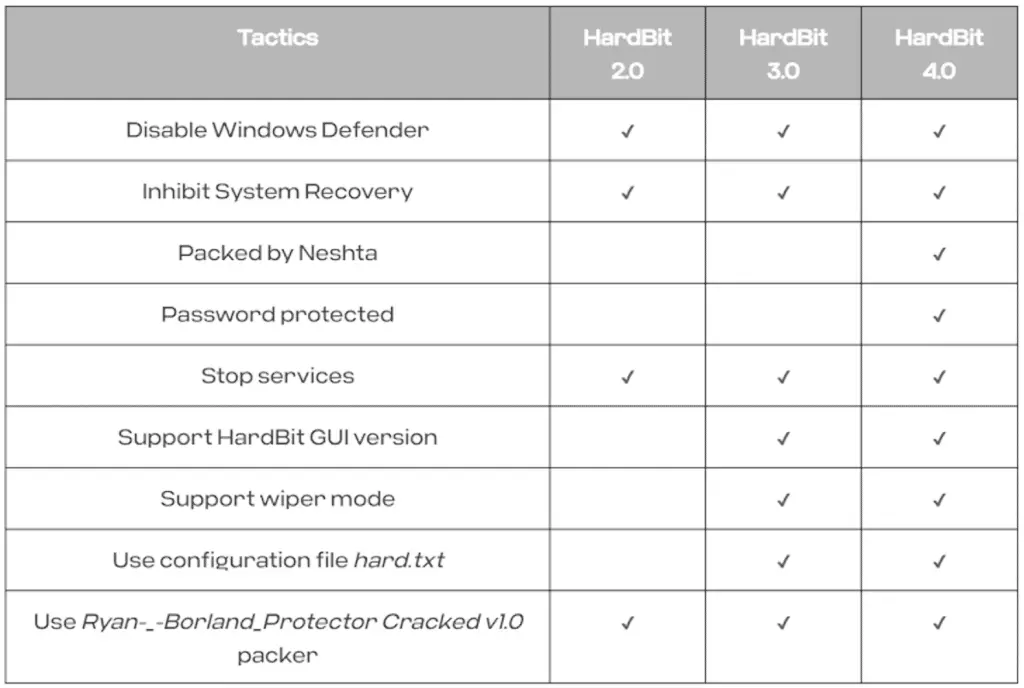
In addition to being offered to operators in the form of command-line or GUI versions, the ransomware requires an authorization ID in order to be successfully executed; the GUI version also supports a wiper mode to irrevocably erase files and clean the disk.
“Once cyber criminals successfully enter the decoded authorization ID, HardBit asks for an encryption key to encrypt files on the targeted machines and proceeds with the ransomware procedure.“, Cybereason noted, adding: “The wiper mode feature must be enabled by the HardBit Ransomware group and the feature is likely an additional option that operators need to purchase. If operators require wiper mode, they should distribute hard.txt, an optional HardBit binary configuration file that contains the authorization ID to enable wiper mode..”
The development comes as cybersecurity firm Trellix has written a detailed report a ransomware attack called CACTUS which has been observed exploiting security vulnerabilities in Ivanti Sentry (CVE-2023-38035) to install file-encrypting malware using legitimate remote desktop tools such as AnyDesk and Splashtop.

Ransomware activity continues to “remain in an upward trend” in 2024, with ransomware authors claiming 962 attacks in Q1 2024, up from 886 attacks reported year-over-year; LockBitAkira and Black Suit emerged as the most prevalent ransomware families during the period, Symantec said.
According to Palo Alto Networks’ 2024 Unit 42 Incident Response report, the average time from compromise to data exfiltration dropped from nine days in 2021 to two days last year. In nearly half (45%) of cases this year, it was less than 24 hours.
“Available evidence suggests that exploitation of known vulnerabilities in public-facing applications continues to be the primary vector for ransomware attacks.,” has said the company owned by Broadcom. “Bring your own vulnerable driver (BYOVD) continues to be a favorite tactic among ransomware groups, particularly as a means of disabling security solutions.”
#HardBit #Malware #Version #Evades #Detection