The fog it’s a meteorological phenomenon which occurs when thehumidity in the air condenses into tiny water droplets, suspended near the ground. This condition creates a sort of “ground level cloud” that can significantly reduce visibilitymaking it difficult to see far ahead. Fog usually forms when there are certain weather conditions, such as high humidity and rapidly cooling air. In this article, we will take a deeper look at what fog is and how it can affect your daily life as a driver.
What is fog?
In the meteorological field we talk about fog when it is present at ground level and the horizontal visibility And less than 1 km ( beyond it is said mist ). This phenomenon indicates the moment in which the air becomes saturated with humidity. Water droplets form in suspension due to the cooling of the atmosphere. Sometimes it also depends on the heat exchange between the ground and the air. This thin layer of humidity suspended in the air can modify completely the perception of the environment surrounding areas, hiding details and accentuating shadows, causing no small amount of problems for drivers.
Types of fog
There are different types of fog, classified according to how they form. The radiation fog occurs mainly during clear, windless nights, when the ground loses heat rapidly through radiation. This cooling causes the moisture near the ground to condense, generating a dense fog. In contrast, the advection fog It forms when a mass of warm, moist air flows over a cooler surface, such as a body of water or cold ground, cooling and condensing into fog. Other types include steam fogwhich is created when cold air passes over warm water, and the climbing fogwhich develops when moist air is lifted up mountain slopes and cools adiabatically.
Tips for dealing with fog
Fog can have significant effects on driving safetyrepresenting one of the most weather conditions dangerous for motorists. The reduction of visibility is the main risk associated with driving in fog. In dense fog, visibility can drop to a few meters, making it difficult to perceive the road, signs and other vehicles. This phenomenon increases the risk of accidents, as drivers may not have enough time to react to unexpected obstacles or to stop in an emergency.
Another problem is the distortion of the perception of distance and speed. Fog can make objects appear farther away than they actually are, causing drivers to underestimate the distance to vehicles ahead. This effect, combined with reduced visibility, can lead to rear-end collisions or skidding. Additionally, the lack of clear visual cues can cause disorientation and loss of direction, especially on unfamiliar or unlit roads.
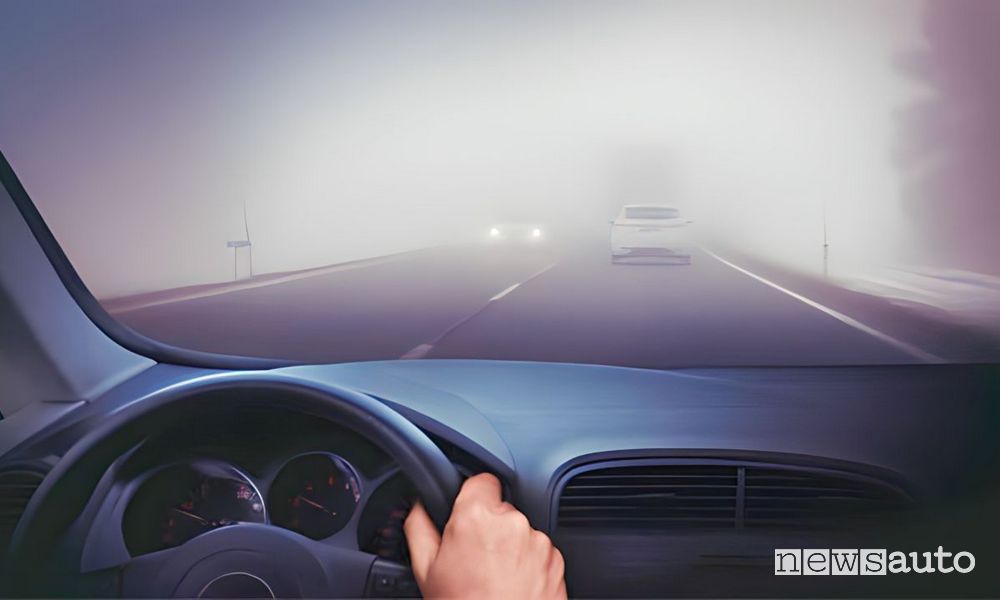

For improve driving safety in foggy conditionsit is essential to adopt some precautions. Reduce speed and maintain a safety distance greater than other vehicles are essential measures to compensate for reduced visibility and reaction time. It is advisable to use the front and rear fog lightsif available, as they are designed to improve visibility in dense fog conditions. However, it is important avoid using high beam headlightswhich can be reflected in the fog and further worsen visibility.
Finally, in case of very dense fog, it is preferable stop in a safe placesuch as a rest area or parking lot, until conditions improve. Remaining cautious and prepared is key to reducing the risks associated with driving in fog.
Signage of the fog
There specific road signs for fog plays a crucial role in the road safetyhelping drivers navigate in conditions of reduced visibility. When fog limits visibility, making it difficult to see the road and other vehicles, well-placed and clearly visible signs can make the difference between safe driving and potentially dangerous driving.

One of the most common tools for signaling the presence of fog are the illuminated road signs or variables. These signs, strategically placed along highways and major roads, can be updated in real time to warn drivers of foggy conditions and recommend reduced speeds. Messages can also include warnings about accidents or traffic jams, providing critical information for making safe driving decisions.
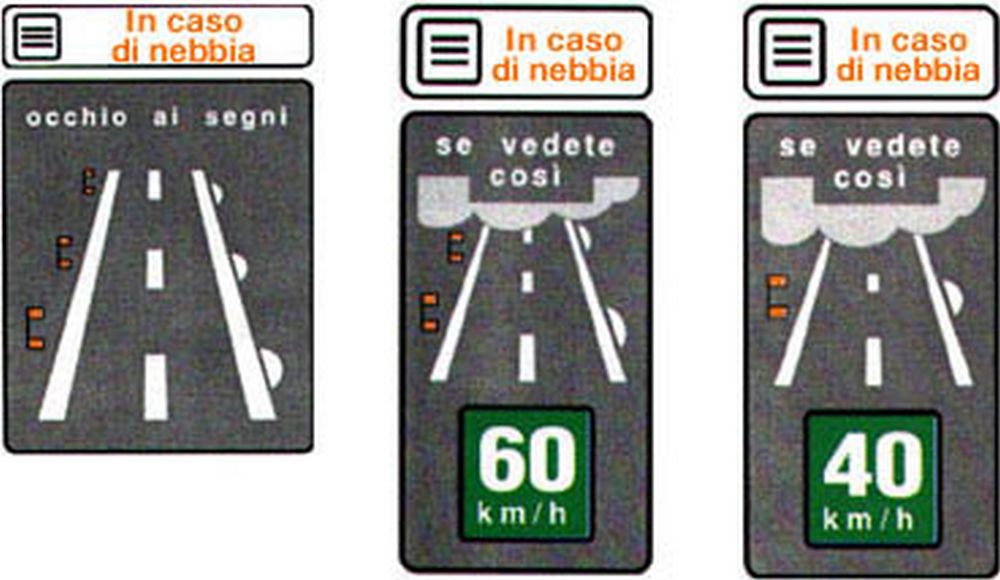
In addition to the light signals, many sections of road are equipped with reflectors or reflective markers on the edges of the road and in dividing lines. These devices reflect the light from the headlights of vehicles, improving the visibility of the road in conditions of heavy fog. Reflectors are often colored differently to indicate different areas of the road: white or yellow ones are located along the edges of the road, while red ones can indicate an imminent danger or the approach of a sharp curve.
In some regions particularly subject to the phenomenon, they can also be installed fog detection systems. These systems use sensors to monitor fog density and automatically activate warning signals and speed reductions. In cases of extremely reduced visibility, they can also temporarily close sections of road to ensure driver safety.
It should also be remembered that the speed limit drops to 50 km/h if visibility drops below 100 metres, which can be calculated using the gutters located along the side of the carriageway, spaced 50 metres apart.
Wanderer above the sea of fog
Speaking of fog, they couldn’t fail to mention the Wanderer above the sea of fog (The Wanderer above the Nebelmeer, in German), an oil painting on canvas by the German Romantic painter Caspar David Friedrich, made in 1818 and preserved at the Hamburger Kunsthalle in Hamburg. The Wanderers were the ancient carters, transporters and street vendors. Today we can define travellers as not only those who walk on foot, but also those who travel by other means, such as cyclists, motorcyclists or hitchhikers.
The wanderer is a symbolic and literary figure that represents a person who wanders or walks without a fixed destination. It is often used as a metaphor for research, inner journey or exploration of life and the world.
→ Read MORE TIPS ON DRIVING IN POOR VISIBILITY
#Fog #road #road #signs
